Transforming Ideas into Reality: The Art of the Prototype Model Maker
The world of design and innovation is a vast landscape where ideas take flight and evolve into groundbreaking products. At the heart of this transformation is the prototype model maker, a skilled artisan who plays an essential role in the product development process. Through a combination of technical expertise, creativity, and craftsmanship, these professionals bring to life the visions of designers, engineers, and architects. In this article, we delve deep into the world of prototype model making, examining its importance, techniques, and the diverse range of applications.
The Role of a Prototype Model Maker
A prototype model maker is not just a builder of models; they are integral to the entire design process. Their responsibilities include:
- Interpretation of Designs: Understanding and translating blueprints or digital files into physical models.
- Material Selection: Choosing appropriate materials that reflect the desired characteristics of the finished product.
- Crafting Prototypes: Skillfully creating models that are accurate representations of the envisaged final product.
- Testing and Modification: Conducting tests on prototypes and making necessary adjustments based on feedback.
- Collaboration: Working closely with designers, engineers, and clients to ensure that models meet specifications and expectations.
Why Prototyping is Essential in Modern Business
In today’s fast-paced business environment, the importance of prototyping cannot be overstated. Here are several reasons why a prototype model maker is a key player in various industries:
1. Visual Communication
Prototypes serve as a tangible means of communication between stakeholders. When ideas are translated into physical form, it becomes easier for teams to visualize the end product. This visual element can foster better discussions, leading to increased collaboration and reduced misunderstandings.
2. User Testing and Feedback
Creating prototypes allows companies to gather valuable user feedback early in the design phase. By presenting a prototype to potential users, businesses can assess the functionality and aesthetic appeal, making adjustments based on real-world insights.
3. Cost Efficiency
Investing in a prototype model maker can save businesses substantial costs in the long run. By identifying flaws and necessary modifications in the prototype stage, companies can avoid costly changes during mass production.
4. Risk Mitigation
Prototyping plays a critical role in risk management. A well-crafted prototype allows for thorough testing and validation of concepts before significant resources are committed to production.
Techniques Used by Prototype Model Makers
The art of prototype making employs a variety of techniques, each tailored to meet specific project needs. Here’s a look at some techniques that a skilled prototype model maker might employ:
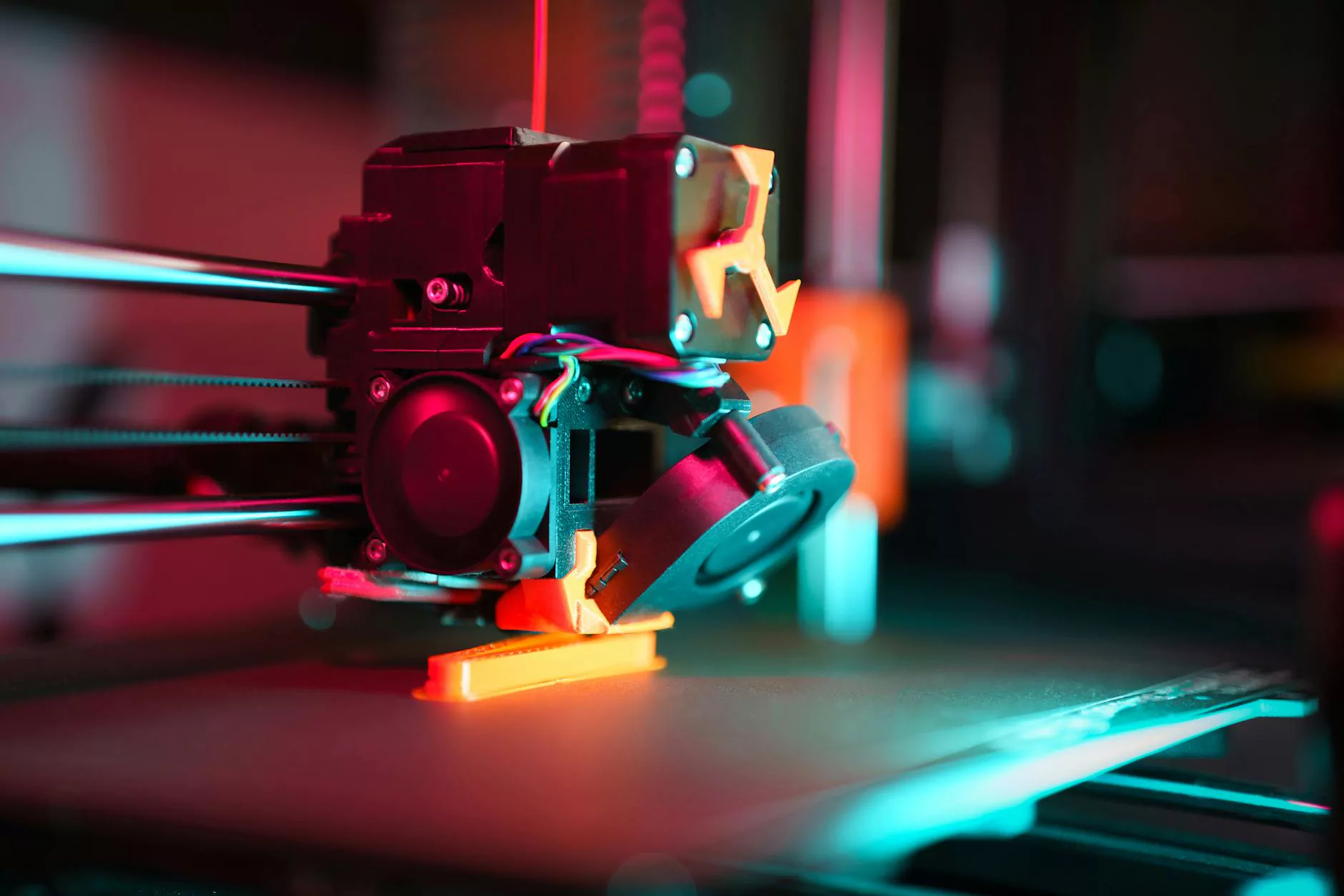
1. 3D Printing
One of the most revolutionary techniques in model making is 3D printing. This technology allows for rapid prototyping, enabling model makers to produce intricate designs with precision. From concept to creation, 3D printing has transformed how designs are manifested.
2. CNC Machining
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining provides high accuracy and repeatability for producing models. This technique employs computer-controlled machinery to carve or mill materials into specified shapes, making it ideal for creating prototypes that require consistent detail.
3. Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is another valuable technique used for creating precise shapes from materials such as wood, acrylic, and metal. This method is particularly effective for producing complex designs rapidly and efficiently.
4. Handcrafting Techniques
Sometimes, the art of handcrafting models offers flexibility and creativity that machines cannot match. Methods such as sculpting, assembly, and finishing by hand can result in unique prototypes that reflect the designer's vision.
Materials Used in Prototyping
The selection of materials is crucial for a prototype model maker. Different projects may require different materials based on factors such as durability, cost, and the desired finish. Common materials include:
- Plastics: Lightweight and versatile, plastics can be easily molded and are often used for various prototypes.
- Wood: A classic choice that offers aesthetic warmth and ease of manipulation for hand-crafted prototypes.
- Metal: For prototypes requiring a high level of durability or a polished finish, metal options such as aluminum and steel may be utilized.
- Foam: Lightweight and easily cut, foam is often used for early-stage models to visualize concepts before pursuing more durable materials.
Applications of Prototype Model Making
The scope of prototype model making is vast, spanning across numerous industries. Here are some prominent applications:
1. Architectural Prototyping
In architecture, model makers create detailed representations of building designs. These prototypes aid architects and clients in visualizing spaces and understanding scale, materials, and functionality.
2. Product Design
In the consumer goods sector, prototype model makers develop samples of new products. This process is essential for evaluating ergonomics, aesthetics, and user interaction before final production.
3. Automotive Industry
The automotive sector relies heavily on prototyping to design and test new vehicle models. Engineers utilize prototypes to identify performance issues and design features efficiently.
4. Medical Device Development
In the medical field, prototypes of devices and equipment are necessary for testing designs for safety and functionality. This rigorous testing phase ensures compliance with regulatory standards.
The Creative Process of Prototype Model Making
The journey from concept to prototype is a dynamic and creative process. Here is a step-by-step breakdown of how a prototype model maker approaches a project:
1. Concept Development
The initial stage involves understanding the client's vision and requirements. It may include brainstorming sessions, sketches, and digital mock-ups.
2. Design Planning
Once the concept is solidified, the model maker devises a plan detailing the materials, techniques, and timeline necessary for construction.
3. Prototype Construction
With plans in hand, the builder moves on to construction. This stage may involve a mix of automated processes and handcrafting techniques to bring the model to life.
4. Evaluation and Feedback
After the prototype is complete, it undergoes testing and evaluation. Feedback is gathered from stakeholders to identify areas for improvement.
5. Revisions and Finalization
Based on the feedback, the prototype may be revised. This iterative process can continue until the final model meets the desired specifications and expectations.
Conclusion: Embracing the Craft of Prototype Model Making
In conclusion, the work of a prototype model maker is essential to transforming abstract ideas into tangible forms. Their expertise not only enhances product development but also plays a vital role in fostering innovation across various industries. By understanding the importance, techniques, and applications of prototype model making, businesses can appreciate the value that these skilled artisans bring to the table. Embracing prototyping can lead to better products, reduced costs, and ultimately, greater success in the marketplace.
For businesses looking to enhance their design and prototyping capabilities, considering a collaboration with a reliable prototype model maker such as maquettes-architecture.fr can be a transformative step in their creative journey.








